Introduction¶
According to Wikipedia,
A Bode plot /ˈboʊdi/ is a graph of the frequency response of a system. It is usually a combination of a Bode magnitude plot, expressing the magnitude (usually in decibels) of the frequency response, and a Bode phase plot, expressing the phase shift.
Note: The code is not specific to RC, you can actually use it for other type of circuits & systems.
Connection¶
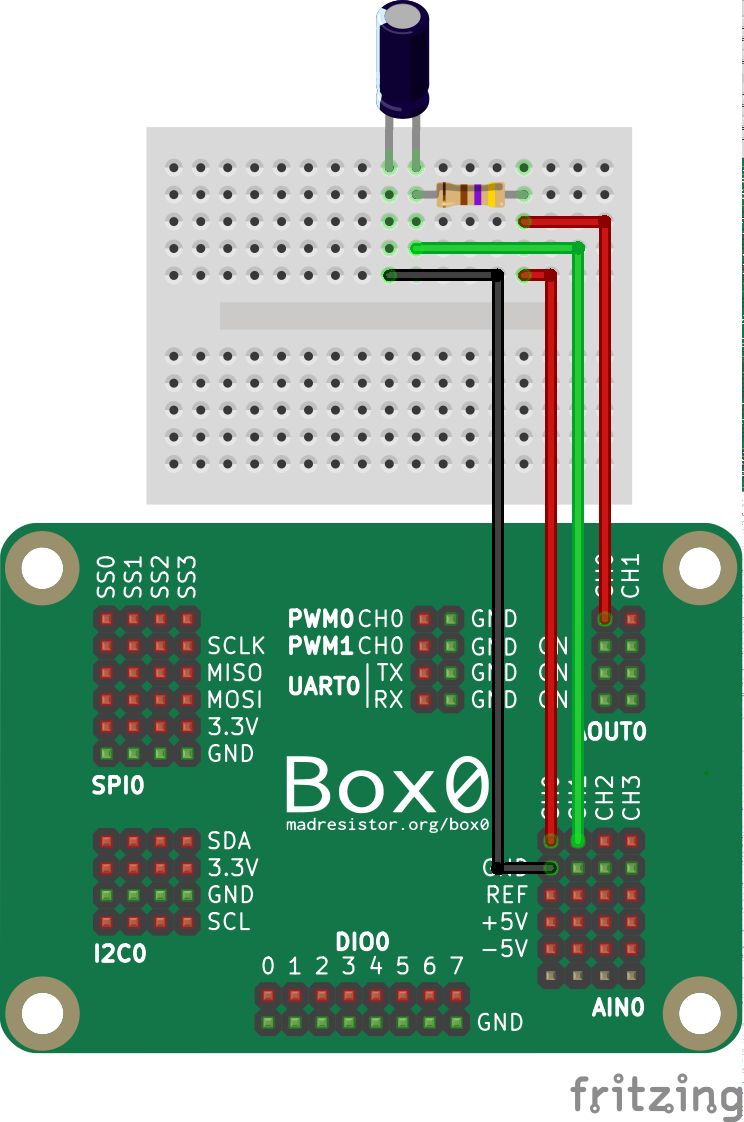 The above is a RC circuit
The above is a RC circuit
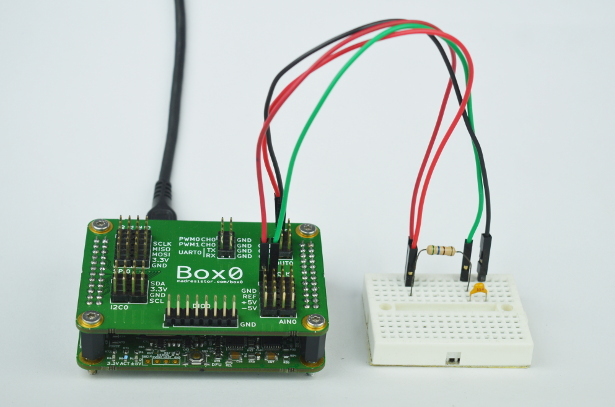
In the circuit, Capacitor = $0.1\mu F$ and Resistance = $550\Omega$.
Using the formula of Cut-off frequency, $f = \frac 1 {2\pi \dot RC}$.
That gives us, $f = \frac 1 {0.000345} = 2.89KHz$
In [3]:
#~ %matplotlib notebook
import box0
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
import math
# allocated resources
dev = box0.usb.open_supported()
ain0 = dev.ain(0)
aout0 = dev.aout(0)
# prepare resources
ain0.snapshot_prepare()
ain0.chan_seq_set([0, 1])
aout0.snapshot_prepare()
aout0.chan_seq_set([0])
FREQ = range(100, 5000, 100)
REF_LOW = -3.3
REF_HIGH = 3.3
INPUT_AMPLITUDE = (REF_HIGH - REF_LOW) / 2
data_freq = []
data_phase = []
data_magnitude = []
def set_freq(freq):
"""
Set frequency to AOUT0.CH0
:param float freq: Requested frequency
:return: Actual frequency
"""
global aout0
# try to stop aout0 from last run
try: aout0.snapshot_stop()
except: pass
# calculate the actual frequency that can be generated
count, speed = aout0.snapshot_calc(freq, 12)
freq = float(speed) / float(count)
# generate a sine wave
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, +np.pi, count)
y = np.sin(x) * INPUT_AMPLITUDE
# set the configuration to module
aout0.bitsize_speed_set(12, speed)
aout0.snapshot_start(y)
return freq
def get_best_speed_and_count(freq):
"""
Find the best sampling frequency at which signal with `freq` can be captured.
Care is taken to not exceed more than 100ms acquisition duration.
:param float freq: Frequency of expected signal that need to be captured
:return: sampling_freq, count
:rtype: int, int
"""
sampling_freq = freq * 40 # atleast sample 40 time more than the signal frequency
max_sample_count = 1000
max_duration = 0.1 # 100ms
sample_count = min(max_duration * sampling_freq, max_sample_count)
# make sample_count multiple of 2, because two channel are being captured
sample_count = int(sample_count / 2) * 2
return int(sampling_freq), int(sample_count)
# ref: http://stackoverflow.com/a/26512495/1500988
def curve_fit_sine(t, y, freq):
"""Perform curve fitting of sine data"""
p0 = (INPUT_AMPLITUDE, 0.0, 0.0)
p_lo = (0.0, -np.pi, 0.0)
p_up = (INPUT_AMPLITUDE, np.pi, REF_HIGH)
def cb(t, amplitude, phase, offset):
return np.sin(2 * np.pi * t * freq + phase) * amplitude + offset
fit = curve_fit(cb, t, y, p0=p0, bounds=(p_lo, p_up))
fit = fit[0]
return fit[0], math.degrees(fit[1])
def get_data(freq):
"""
Get channel data of ain0.
:param float freq: expected Frequency of the signal that need to be captured
:return: magnitude_in_db, phase_in_degree
"""
global ain0
# retrive data
sampling_freq, sample_count = get_best_speed_and_count(freq)
ain0.bitsize_speed_set(12, sampling_freq)
data = np.empty(sample_count)
ain0.snapshot_start(data)
# process the data
t = np.linspace(0.0, float(sample_count) / sampling_freq, sample_count, endpoint=False)
input_amplitude, input_phase = curve_fit_sine(t[0::2], data[0::2], freq)
output_amplitude, output_phase = curve_fit_sine(t[1::2], data[1::2], freq)
# extract results
magnitude = 20 * math.log10(output_amplitude / input_amplitude)
phase = (output_phase - input_phase) % 360
# convert phase into a value that is around 0
if phase < -180:
phase += 360
elif phase > 180:
phase -= 360
return magnitude, phase
for freq in FREQ:
#print("capturing ", freq)
# do the main part!
freq = set_freq(freq)
magnitude, phase = get_data(freq)
# store the results
data_freq.append(freq)
data_magnitude.append(magnitude)
data_phase.append(phase)
# free up resources
ain0.close()
aout0.close()
dev.close()
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, sharex=True)
fig.suptitle("Bode Plot")
magnitude = axs[0]
magnitude.grid(True)
magnitude.set_xscale('log')
#magnitude.set_yscale('log')
magnitude.set_xlabel("Frequency (Hz)")
magnitude.set_ylabel("Magnitude (dB)")
magnitude.plot(data_freq, data_magnitude, 'r.-')
phase = axs[1]
phase.grid(True)
phase.set_xscale('log')
phase.set_xlabel("Frequency (Hz)")
phase.set_ylabel("Phase (Degree)")
phase.plot(data_freq, data_phase, 'r.-')
# Show the data
plt.show()